IDEAS: THE REGULATION OF E-MONEY IN TURKEY
In recent years, E-Money has been gaining traction as a viable alternative payment method to conventional cash both in Turkey and abroad.
At first, each company started online payment methods by integrating its software within their own websites. However, they required separate semi-agreements with each bank. They also charged monthly membership fees, POS machine maintenance fees, and took a commission from each bank. If the customer’s bank did not have an agreement with a credit card, the customer could receive payment from that website.
Entrepreneurs saw this problem as an opportunity, and their solution was led to the birth of the E-Money payment system.
Paypal, now a household name, is just one of the many examples of E-money payment systems in use today. All you need to do is sign up and link your bank to use their platform.
Then came the next generation payment system: VENMO. Without the need for IBAN and other bank information, people could send and receive money with nothing more than a username. If users did not receive their money within three days, VENMO dropped their commission fees.
Welcome to the E-payment system revolution!
Other big companies soon jumped on the bandwagon. In addition to Paypal, we now have ApplePay, Facebook Messenger, and GooglePay.
One should also mention that the E-Money payment system Square, owned by the founder of Twitter, is incredibly popular with vendors and online retailers throughout the United States. The main difference being that Square implements its own special cash register machine, which enabled them to tap into the lucrative sales sector.
E-MONEY IN TURKEY:
Turkey is home to one of the world’s highest users of the Internet and social media. Unsurprisingly, credit card usage rates in Turkey are some of the highest in the World. As a result, online payment methods have the potential for spectacular growth.

Several companies set up shop in Turkey before the government introduced e-money legislation. Once regulations were ratified and enforced, some companies were able to obtain licenses, whereas others were forced to leave the market.
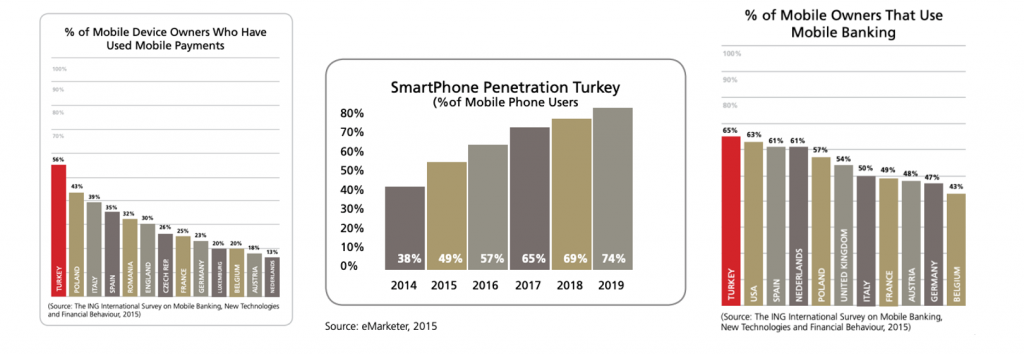
The payment and electronic money services industry is a newly regulated market in Turkey. Now that the regulators have started issuing licenses to operators and service providers, the industry is expected to grow exponentially over the next few years.
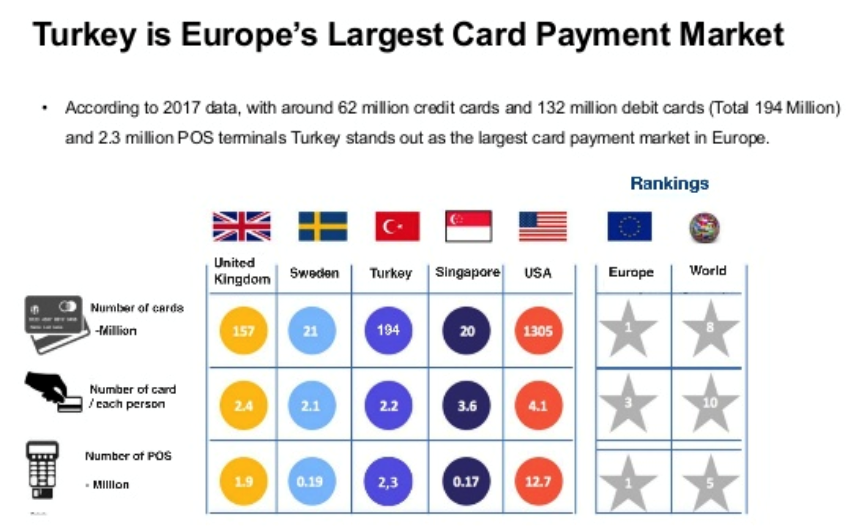
- Turkey is Europe’s Largest Card Payment Country.
E-MONEY LAW IN TURKEY:
In Turkey, principles and procedures regarding payment institutions and electronic money institutions are regulated under Law No. 6493 and the Regulation on Payment Services and Electronic Money Issuance and Payment Institutions introduced by the Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency (BRSA).
2013 : Law No 6493 on Payment and Security Settlement Systems, Payment Services and Electronic Money (“Payment Services Law”)
The regulation is the secondary legislation of Law No. 6493 on payment services and e-money institutions which came into force in June 2013. Law No. 6493 was drafted based on the European Electronic Money Directive.
2014 : The Regulation on Payment Services and Electronic Money Issuance and Payment (“Payment Services Regulation”)
June 27, 2014, 29043 – Bylaw
June 27, 2014, 29043 – Communique
The Communiqué on the Management and Supervision of Information Systems of Payment Institutions and Electronic Money Institutions, which entered into force after being published in the Official Gazette
Europe’s new Payment Services Directive II (“PSD2”)
An electronic money institution intending to issue electronic money under the scope of this Law can operate provided that it is granted permission by the Board.
BOARD : Banking Regulation and Supervision Board ( BRSA ) Turkish: BDDK
Business Models Under Law No. 6493
- Electronic Money
- Prepaid Cards
- Prepaid Accounts
- Virtual Pos Services
- Virtual Marketplace Model
- Sub-Merchant Model
- Money Transfer Services
- Bill Payment Services
Electronic Money: It is defined as the monetary value that is accepted by the real and legal persons other than the electronic money issuing institution and used to perform the payment transactions defined in this Law.
Electronic Money Establishment: A legal person or entity authorized to issue electronic money under the Law.
Other Relevant Laws And Regulations:
- Financial Crimes Investigation Board
- Laundering Crimes
- The Terror Financing Crime
- Law on Protection of Personal Data
- Other laws and sub-regulations
Cryptocurrency & E-money Situation:
CryptocurrencLaws not recognized under Turkish law. That is why Cryptocurrency does not fall within the scope of Law no — 6439 on Payment Securities Settlement Systems, Payment Services, and Electronic Money Institutions. There is currently no legislation that is specifically designed to refer to Cryptocurrency, and therefore it is not entirely accurate to declare this type of business activity.
LICENSED COMPANIES IN TURKEY:
There are 17 active e-money institutions listed by the Turkish Banking Regulation and Supervision Agency (“BRSA”) in Turkey.
| 1.1.2.1 1. | AKÖDE ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | – |
| 2. | BELBİM ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | http://www.belbim.com.tr |
| 3. | BİRLEŞİK ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ VE ELEKTRONİK PARA A.Ş. | http://www.birlesikodeme.com |
| 4. | CEMETE ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | http://www.cemete.com.tr |
| 5. | D ÖDEME ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | https://www.hepsipay.com/ |
| 6. | ERPA ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ VE ELEKTRONİK PARA A.Ş. | – |
| 7. | HIZLIPARA ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ VE ELEKTRONİK PARA A.Ş. | https://www.payporter.com/ |
| 8. | İNİNAL ÖDEME VE ELEKTRONİK PARA HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | https://www.ininal.com/ |
| 9. | İYZi ÖDEME VE ELEKTRONİK PARA HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | https://www.iyzico.com/ |
| 10. | OZAN ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ VE ELEKTRONİK PARA A.Ş. | – |
| 11. | PALADYUM ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | https://www.peppara.com/ |
| 12. | PAPARA ELEKTRONİK PARA ve ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | http://www.papara.com |
| 13. | SİPAY ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | – |
| 14. | TURK ELEKTRONİK PARA A.Ş. | http://www.turkpara.com.tr |
| 15. | TURKCELL ÖDEME VE ELEKTRONİK PARA HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | – |
| 16. | VODAFONE ELEKTRONİK PARA VE ÖDEME HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | http://eparahizmetleri.com |
| 17. | WİRECARD ÖDEME VE ELEKTRONİK PARA HİZMETLERİ A.Ş. | http://www.wirecard.com.tr |
THE E-MONEY INSTITUTION IS SUBJECT TO THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS OF ELIGIBILITY;
- It is required to be founded in the form of a JOINT-STOCK COMPANY,
- Shareholders owning ten percent or more of the capital and holding control is necessary to meet the bank founder qualifications laid down in the Banking Law Nr.5411.
- Its shares should be issued against cash and to name,
- Its paid-up capital, consisting of money and free of all kinds of fictitious transactions, should not be less than 5 MILLION TURKISH LIRAS,
- It is required to have management, adequate personnel and technical pieces of equipment needed for performing the transactions under the scope of this Law and departments handling complaints and objections,
- It is required to take precautions as are necessary for the continuity of the operations to be conducted under the scope of this Law and for the preservation of security and confidentiality of the funds and information related to the electronic money users,
- It is required to have a transparent and open partnership structure and organizational chart that will not constitute an obstacle for the efficient supervision of the Agency.
IMPORTANT NOTES :
- To keep collaterals in the Central Bank region if requested by BRSA,
- Payment irregularities, fraud transactions, commonly known as fraud transactions.
- Not engaged in any payment service or electronic money export activity.
- To keep all information, documents and records open to audit about the transactions they perform and mediate,
- The users of information systems in Turkey for authentication and security in the information security and risk management as open combat with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards at (PCI-DSS)
- The Financial Crimes Investigation Board (MASAK) design aims to think with crimes such as money laundering and the financing of terrorism; Notification of suspicious transactions to MASAK, the identity of the personnel he serves, and the need to be an internal compliance officer.
What to do to open an e-money licensed company in Turkey:
– Open the JSC in Turkey
– Trade Registry
– Notary Transactions
– Increasing Company Capital
– Preparation of the application form for the license
– Following the process from beginning to end
– Preparation of the articles of association and Preparation of all related contracts
– Preparation of the Minutes of the Board Meeting
– Preparation of Activity Certificate
– Contacting relevant institutions
– Tax office applications
– Bank applications
You can see that the future payment system will be in the hands of companies that have e-money licenses.
Obtaining a license also makes you lend you credibility in the eye of the customer. The world of online credit card usage in Turkey is very high, which means there’s more potential to use e-payment services in the future.
It may have the opportunity to take part, and the Turkish market might be your next best investment. However, we recommend that you work with a reputable law firm and consult competent experts before making your final decision,
Atty.Sima BAKTAŞ
Founder / Lawyer
GlobalB Law
globalblaw.com
GlobalB Law has represented financial institutions, governmental bodies and regulatory agencies since 2014. Our practice areas are extensive, with an emphasis on emerging technologies. As a member firm of New York-based CKR Law LLP, our global outreach spans four continents and 30 countries.
GLOBALB LAW FIRM
INTERNATIONAL LAW FIRM BASED IN NEWYORK www.ckrlaw.com
BARBAROS BULVARI 31/9 BEŞİKTAŞ – İSTANBUL – TURKEY
00902122588121 / 00905324007381
www.globalblaw.com / globalb@globalblaw.com
